#AudioCation #2: DRIVERS 101 by Treble Well Xtended
Understanding Drivers in IEMs and Headphones: Simplified
Drivers are crucial components in IEMs and headphones, as they convert electrical signals into the sound we hear. This article is an attempt to explain the most common driver types and their configurations. #Audiophile #Learning
What Is a Headphone/IEM Driver?
A headphone driver is a transducer that transforms electrical energy into acoustic energy (SOUND). It is basically a small speaker inside your headphones or IEMs that generates sound by moving air to create pressure waves, which your ears perceive as sound. The size and type of driver can significantly affect the sound quality and overall performance of your headphones.
Types of Drivers
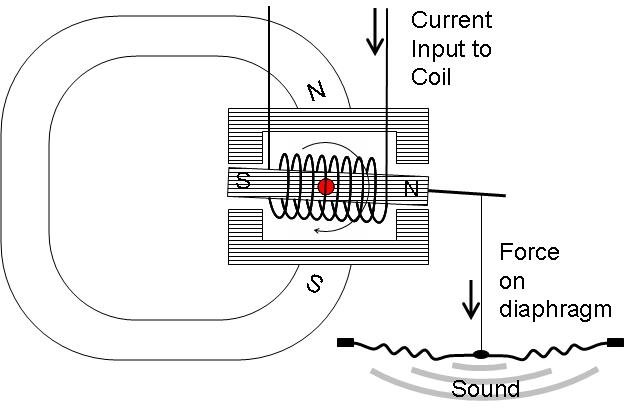
1. Dynamic Drivers
How They Work: Dynamic drivers, also known as moving coil drivers, are the most common type. They use a magnetic field created by a fixed magnet that interacts with a voice coil carrying an electrical signal. The voice coil moves in response to the signal, pushing and pulling a diaphragm, which vibrates and produces sound.
Pros:
Affordable: Cost-effective and widely accessible.
Durable: Robust and suitable for various listening environments.
Versatile: Offers a balanced sound for different music genres.
Cons:
Potential Distortion: May produce unwanted resonances or distortion at higher volumes.
Dynamic drivers are popular for their good balance between cost and performance. They may not deliver the most accurate sound, but they’re more than sufficient for most users, especially in consumer-grade headphones.
Some Notable Single DD IEMs: Tangzu Wan’er, Truthear Zero Red, Simgot EA1000, Sennheiser IE200, IE600, IE900, Softears Twilight.
2. Planar Magnetic Drivers
How They Work: Planar magnetic drivers use a flat diaphragm embedded with electrical conductors between two magnets. This setup allows for very precise movement, resulting in clear, fast, and detailed sound.
Pros:
Lower Distortion: More accurate sound reproduction.
Smooth Response: Natural sound across a wide frequency range.
Cons:
Heavier: Bulkier and heavier than dynamic drivers.
More Expensive: Often requires an external amplifier.
Planar magnetic drivers are ideal for audiophiles who prioritize sound quality and don’t mind the extra weight and cost.
Some Notable Planar IEMs: Artti T10, NiceHCK F1 Pro, Letshuoer S12, Hidizs MP145, 7Hz Timeless, Letshouer S15 etc.
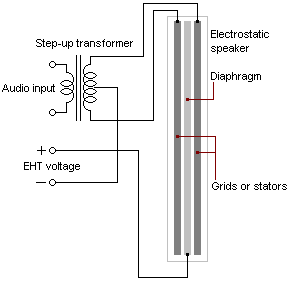
3. Electrostatic Drivers
How They Work: Electrostatic drivers use a thin, electrically charged diaphragm placed between two perforated metal plates. When an audio signal is applied, the diaphragm moves back and forth, creating sound waves.
Pros:
Extremely Accurate: Minimal distortion and highly accurate sound reproduction.
High Fidelity: Ideal for high-end audio applications.
Cons:
Expensive: Requires a specialized amplifier and is costly.
Bulky: Less practical for everyday use.
Electrostatic drivers are the pinnacle of audio technology but are primarily targeted at enthusiasts due to their high cost and specialized equipment requirements.
Some Notable EST IEMs: Generally best used with DD and BAS like in Moondrop Variations, HiSenior Meg5EST, Thieaudio Monark MKII etc.
4. Balanced Armature Drivers
How They Work: Balanced armature (BA) drivers use a small magnetic armature suspended between two magnets. The armature moves in response to an audio signal, causing the diaphragm to vibrate and produce sound.
Pros:
Small and Efficient: Ideal for IEMs and hearing aids.
Excellent Treble: Great high-frequency response with the ability to use multiple drivers for different frequency ranges.
Cons:
Limited Bass: Not very efficient at handling the full audio spectrum with a single driver.
Balanced armature drivers excel in high-frequency reproduction, making them a popular choice for multi-driver IEMs, especially for mids and treble.
Some Notable BA IEMs: Aful Magic One, Etymotic ER4SR, Softears Studio 4, Symphonium Metor, 64 Audio U12T
5. MEMS Drivers
How They Work: Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) drivers use the piezoelectric effect, where certain materials become electrically polarized under mechanical stress, causing them to change shape and produce sound waves.
Pros:
Tiny and Lightweight: Less than 1mm thick, making them ideal for compact devices.
Fast Response: Low distortion and efficient at high frequencies.
Cons:
Requires Special Circuitry: Still emerging in the consumer market.
MEMS drivers represent the future of headphone technology, offering the potential for even smaller and more efficient audio devices.
Some Notable Single DD IEMs: Noble Audio XM1, and mostly coming in new TWS like Creative Aurvana Ace 2, Noble Audio Falcon Max
Types of Driver Configurations in IEMs
Single Dynamic Driver: Offers a simple, often warm sound signature.
Multiple Dynamic Drivers: Used to achieve enhanced bass response or a wider frequency range.
Single Balanced Armature Driver: Provides a clear, detailed sound but may lack bass impact.
Multiple Balanced Armature Drivers: Allows for precise tuning of different frequency ranges.
Hybrid: Combines dynamic and balanced armature drivers to leverage the strengths of both, sometimes incorporating a special crossover for an enhanced sound profile.
Tribid: Combines dynamic and balanced armature drivers with electrostatic (EST) or piezoelectric (PZT) drivers to further enhance sound clarity and fidelity.
Multi-Driver Configurations: Incorporates multiple drivers of the same or different types to achieve complex sound signatures.
Factors That Can Affect Driver Performance
Driver Size and Material: The size and material of the diaphragm significantly impact sound quality.
Crossover Design: The way different drivers are combined in hybrid configurations affects the overall balance.
Enclosure Design: The IEM's housing influences the driver's performance and soundstage.
Which Driver Type Is the Best?
While headphone preferences are subjective, dynamic drivers often represent a solid middle ground. For most users, dynamic drivers provide a great balance of cost, durability, and sound quality.
However, if you’re an audiophile with a passion for high-fidelity sound, exploring other driver types could lead you to new levels of audio excellence. And you can always revisit this guide to understand your needs.